We have learned that the pH is calculated by the following formula:
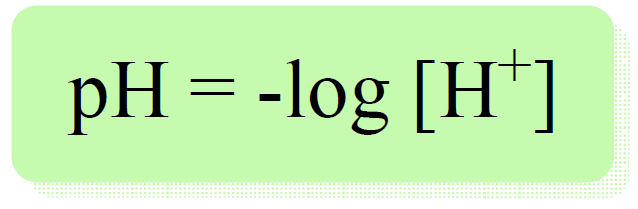
To calculate the concentration of H+ or H3O+ hydronium ion from pH, we take the antilog of the pH, that is 10 to the negative power of pH.
For example, calculate the hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution with a pH of 5.64 at 25°C.
pH = -log [H3O+], [H3O+] = 10-pH = 10-5.64 = 2.29 × 10-6 M
Check Also
- Definitions of Acids and Bases
- Acid-Base Reactions
- Acid-Base Titrations
- Conjugate Acid and Conjugate Base
- Autoionization of Water and Kw
- The pH and Acidity
- Acid Strength, Ka, and pKa
- Base Strength, Kb, and pKb
- Ka, pKa, Kb, and pKb Relationship
- The pH of a Strong Acid and Base
- pH + pOH = 14
- The pH of a Weak Acid
- The pH of a Weak Base
- The pH of Polyprotic Acids
- The acidity of a Salt Solution
- The pH of a Salt Solution
- The pH of Salts With Acidic Cations and Basic Anions
- pH Practice Problems
- Acids and Bases Practice Problems
Acids and Bases Quiz