In the previous post, we talked about electron configurations, what they show, how to read, and how to write them based on energy levels and sublevels.
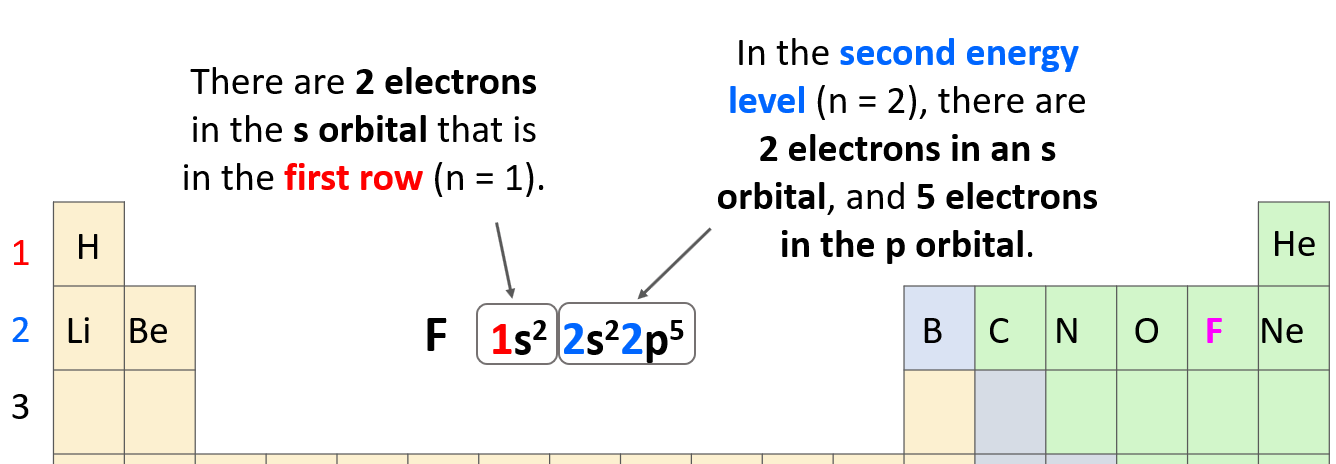
As a reminder, electron configurations show the number and location of electrons in an atom or an ion. For example, the electron configuration of fluorine is1s22s22p5.
The number before each letter indicates the main energy level, and this is the principal quantum number, n. The letters (s, p, d, f) tell us the type of the orbital, and the exponent is for the number of electrons.
The 1s2 means there are 2 electrons in the s orbital that is in the first row. Next, we have the orbitals in the second energy level because fluorine is in the second row of the periodic table. In this level, there are 2 electrons in an s orbital, and 5 electrons in the p orbital:
This is the very least you should know in addition to the order of filling the energy levels and sublevels so please go over the detailed post on the electron configurations before getting to ions.
Electron Configuration of Ions
The first thing you need to remember here is that cations are formed by losing an electron(s), and anions are formed by gaining an electron(s).
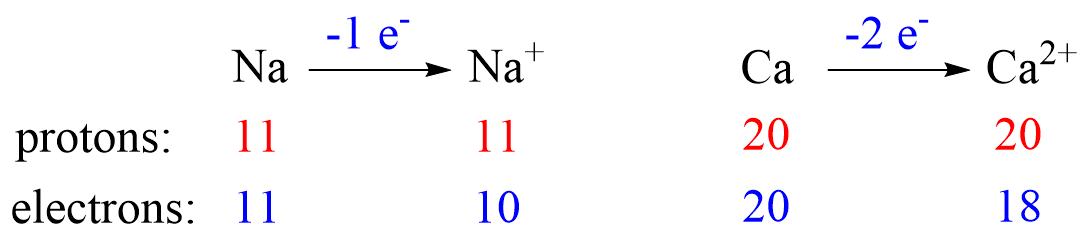
The charge of the ion is a result of an imbalance between the number of protons and electrons. If it is a cation, then the positive indicates how many more protons it has compared to the number of electrons. For anions, the charge tells how many extra electrons there are compared to the number of protons.
Recall, this pattern for the formation of anions and cations: Metals tend to lose electron(s) and become cations (positively charged ions).
Nonmetals tend to gain an electron(s) and become anions (negatively charged ions).
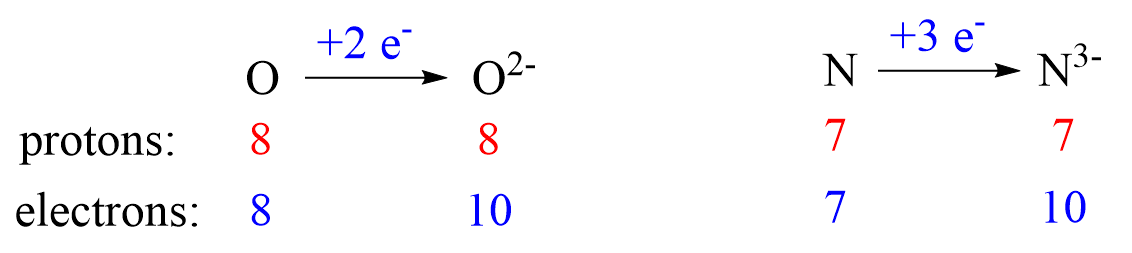
Notice that the number of protons is not changed, and the ions are charged because, unlike atoms, their number of protons and electrons is not equal.
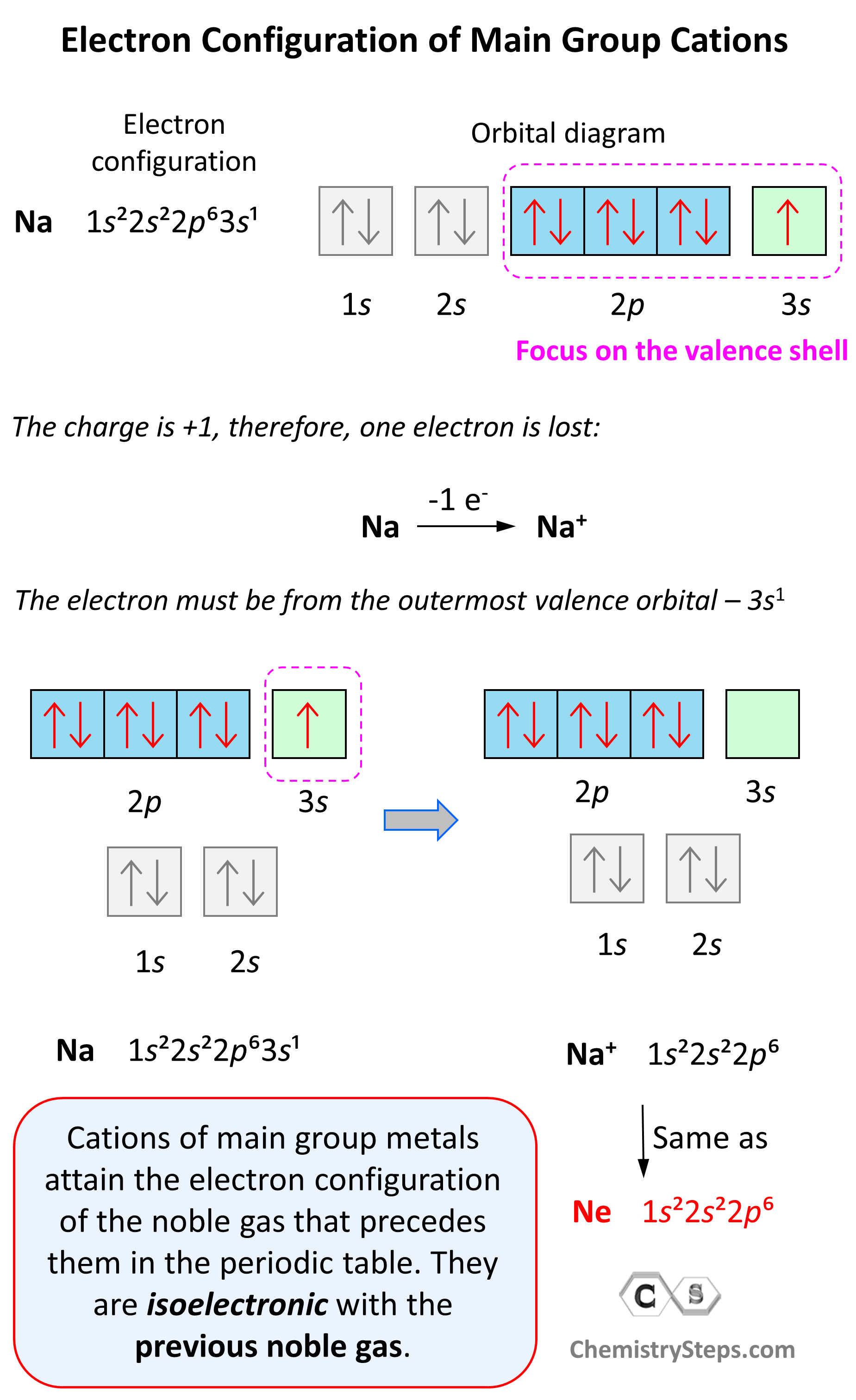
Electron Configuration of Main Group Cations
Now, how do we determine the electron configuration of an ion? If it is, for example, a +1 charged cation, that means the atom has lost one electron. This electron is going to be from the outermost valence shell as these are the electrons farthest away from the nuclei and thus not as strongly attracted to it.
Let’s see an example on Na. It is in the first group, so it loses one electron to become Na+. The electron configuration of sodium is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹, and the electron is removed from the energy level with the greatest n value – 3s. Therefore, the electron configuration of the Na+ ion will be 1s²2s²2p⁶:
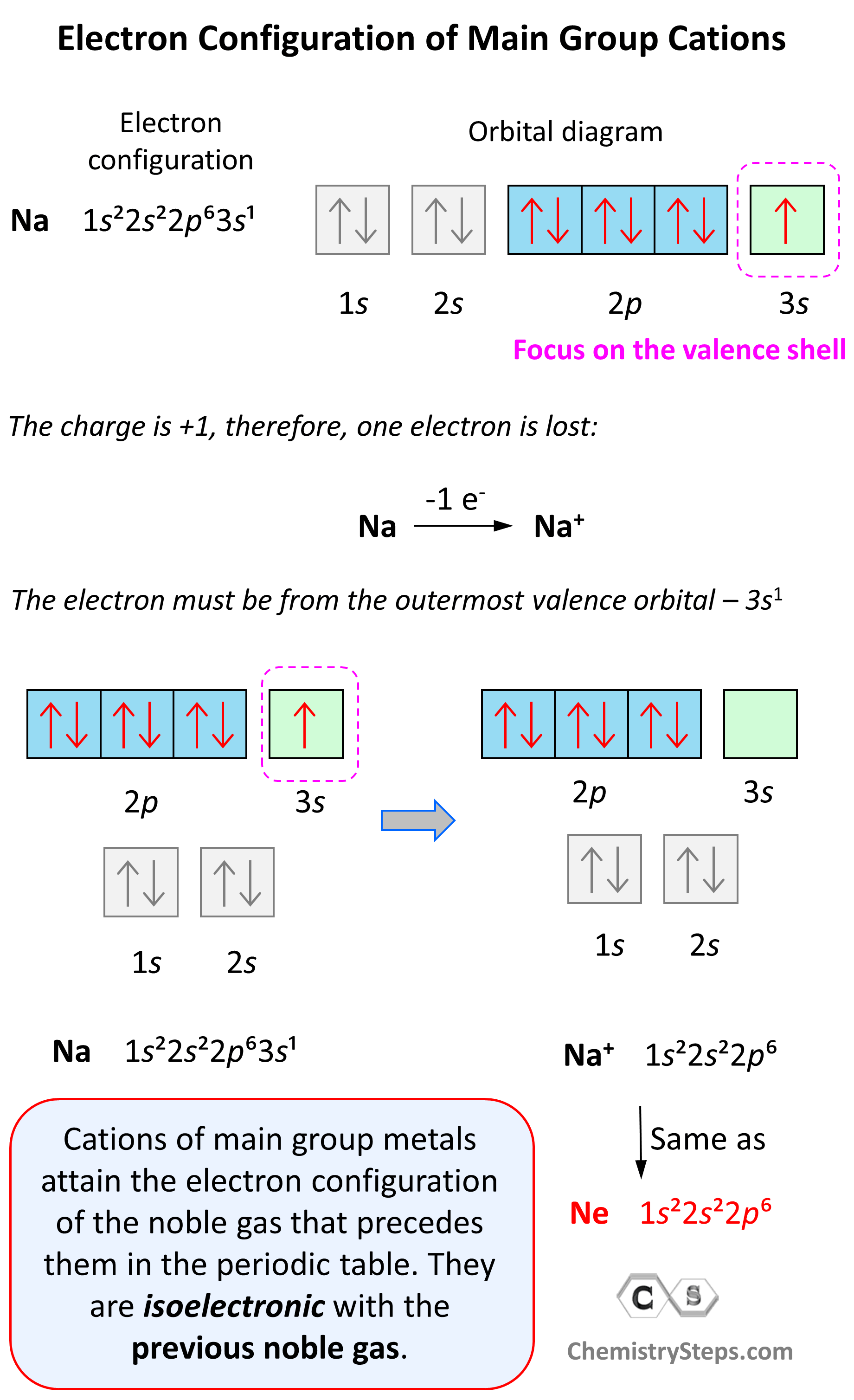
Notice that the ion has a configuration with a complete shell of p orbitals which is characteristic of noble gases. In fact, this is the electron configuration of Ne, and we say that Na+ and Ne are isoelectronic (same electronic structure). The reason for this is that, remember, noble gases are very stable because of the low energy level of complete orbitals.
Na (1s22s22p63s1) ⟶ e− + Na+([He]2s22p6) [isoelectronic with Ne ([He] 2s22p6)]
Let’s now determine the electron configuration of the Ca2+ ion. It is formed when an atom of Ca (1s22s22p63s23p64s2 or [Ar]4s2) loses two electrons from the outer shell 4s.
Ca ([Ar]4s2) ⟶ 2e− + Ca2+([Ar]) [isoelectronic with Ar]
This pattern explains why the metals in the first group become +1, the ones in the second group become +2, and Al, for example, becomes +3. It takes removing one electron from a metal in the first group to obtain the electron configuration of the previous noble gas, it takes two for the group two metals, etc.
Electron Configuration of Anions
Anions are formed when the atom gains as many electrons as necessary to attain the electron configuration of the next noble gas in the periodic table. For example, oxygen is in group 6, and therefore, it will need two electrons to attain the electron configuration of Ne:
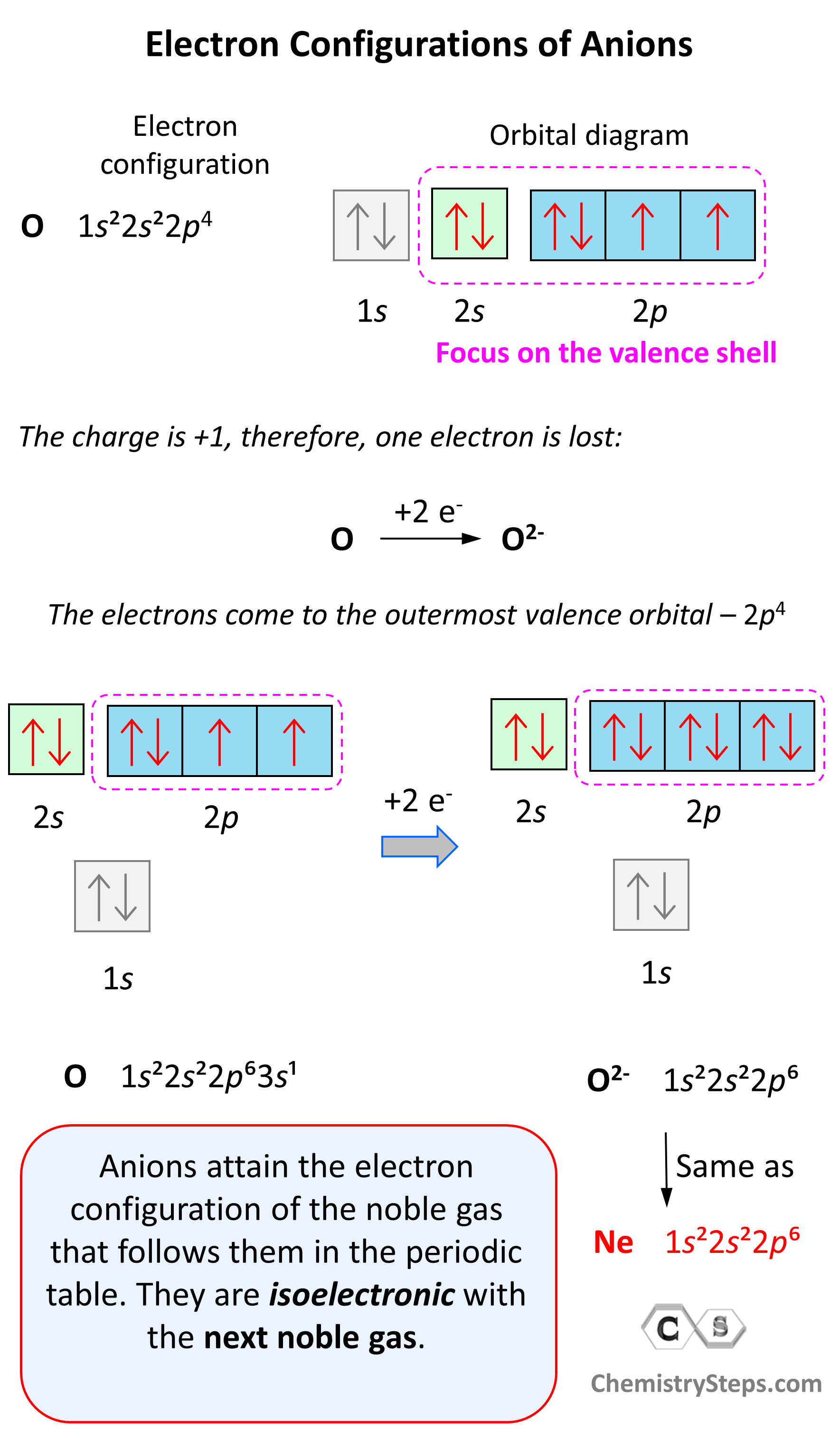
Notice again that the two electrons go to the outermost valence orbital. Oxygen has 6 valence electrons – those in the 2s and 2p orbitals, however, since p sublevels are higher in energy, and they are the only ones capable of accepting additional electrons, the two electrons go to the 2p orbitals. The electron configuration of the oxide ion (O2-) is therefore, 1s²2s²2p⁶.
O (1s22s22p4) + 2e−⟶ + O2- ([He]2s22p6) [isoelectronic with Ne ([He] 2s22p6)]
Another common type of monoatomic anions are the halides. Halogens are in group 7, and therefore, they only need one electron to attain the electron configuration of the noble gas following them in the periodic table. For example, bromine takes one electron and becomes isoelectronic to t Kr:
Br([Ar] 4s23d104p5) + e− ⟶ Br−([Ar] 4s23d104p6) [isoelectronic with Kr ([Ar] 4s23d104p6)]
Electron Configuration of Transition Metal Cations
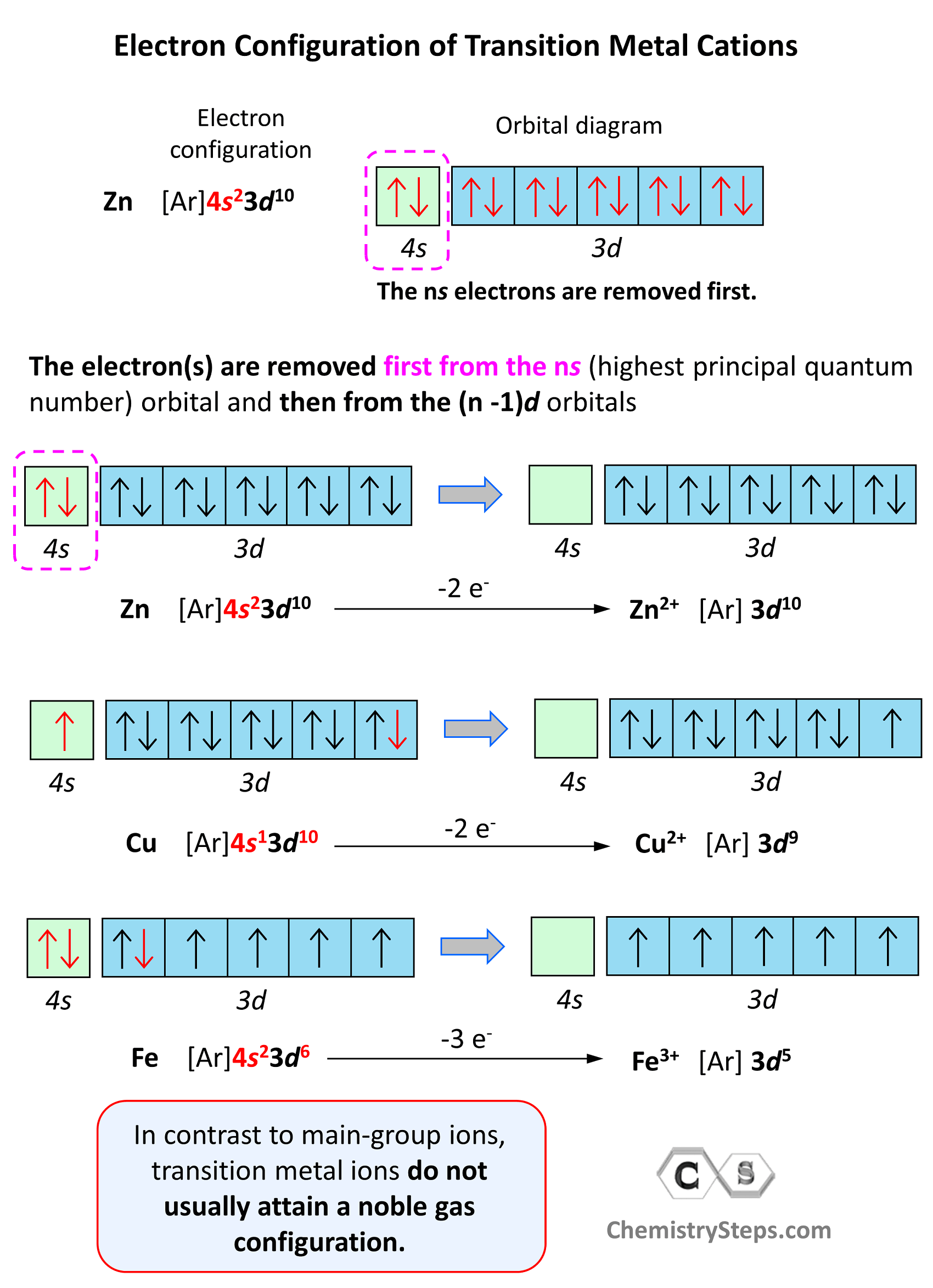
In contrast to main-group ions, transition metal ions do not usually attain a noble gas configuration. This is because the ns level is the outermost level, and the (n-1)d is considered an inner level therefore, it will take too much energy to remove those electrons and achieve a noble gas configuration. Therefore, the cation of a transition metal is formed by removing first the electrons from the ns (highest principal quantum number) orbital and then from the (n -1)d orbitals.
For example, the electron configuration of Zn is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d10 or [Ar]4s23d10, and it loses the two electrons from the 4s orbital to become Zn2+[Ar]3d10. This is “not a bad” electron configuration considering the filled d orbitals.
Check Also
- Atomic Orbitals
- Electron Configurations
- Orbital Diagrams
- Aufbau’s Principle, Hund’s Rule, and Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
- Hund’s Rule
- Pauli Exclusion Principle
- Quantum Numbers (n, l, ml, ms)
- Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
- Rydberg Formula
- The Photoelectric Effect
- Calculating The Energy of a Photon
- Effective Nuclear Charge
- Atomic Radius
- Ionic Radius
- Ionization Energy
- Electron Affinity
- Energy, Wavelength, and Frequency Practice Problems
- Electronic Structure of Atoms Quiz
- Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
Practice
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy one p orbital?
a.14
b. 2
c. 10
d.1
e. 6
The n = 2 shell can accommodate a maximum of ____ electrons.
A. 10
B. 8
C. 4
D. 6
E. 2
Which of the following is an incorrect orbital occupancy representation?
- 4d3
- 3d5
- 2s3
- 1s1
- 2p2
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in 3s subshell is
- 10
- 2
- 6
- 1
- 8
The following electron configuration is incorrect:
- 1s22s2
- 1s22s32p3
- 1s22s22p5
- 1s22s22p4
- 1s22s22p63s2
Which electron configuration represents an excited state of the indicated atom?
- He: 1s2
- Na: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 3s1
- P: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
- N: 1s2 2s2 2p23s1
- Ne: 1s2 2s2 2p6
Which of the following represents the ground state electron configuration of a transition element?
- 1s22s22p63s23p5
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d104s1
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p4
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s2
- 1s22s22p3
Which of the following is the correct ground-state electron configuration of V is?
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d3
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d5
- 1s22s22p63s24s23d3
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d5
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3
Which of the following represents a possible excited-state electron configuration for an iron atom?
- [Ar]3d74s2
- [Ar]3d64s2
- [Ar]3d74s1
- [Ar]3d64s1
- [Kr]3d74s1
Each of the following is an accurate representation of ground-state electron configuration except:
- Fe: [Ar]4s23d6.
- Ca: [Ar]4s2.
- Se: [Ar] 4s23d104p4.
- Ag: [Kr] 5s24d9.
- Ti: [Ar] 4s2 3d2
How many electrons, in total, are present in p orbitals in a ground-state nickel atom?
- 8
- 12
- 6
- 24
- 3
Which one of the following represents electron configuration of an excited carbon atom?
- 1s22s22p3
- 1s22s22p1
- 1s22s22p13s1
- 1s22s23s1
- 1s22s22p2
Which of the following ground-state electron configurations is incorrect?
- Cl: [Ne]3s23p5
- Ge: [Ar] 4s2 3d103p2
- Co: [Ar]4s23d7
- Rb: [Kr]5s1
- Mn: [Ar] 4s23d5
What is the ground-state electron configuration of chromium (Cr)?
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p4
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d10
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s23d4
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d6
What is the ground-state electron configuration of bromine (Br)?
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 4p5
- [Kr] 4s23s104p5
- [Ne] 3s2 3p5
- [Ar] 4s23d104p5
- 1s2 2s2 2p5 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5
The ground state electron configuration of As is ________.
- 1s22s23s23p64s23d104p2
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p1
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104d3
- [Kr]4s23d104d3
Which of the following elements has the same valence-shell electron configuration as lithium?
- calcium.
- sulfur.
- potassium.
- magnesium.
- argon.
How many unpaired electrons are found in the d orbital of nickel.
- 4 electrons
- 3 electrons
- 2 electrons
- 8 electrons
- none of these
The ground-state electron configuration of the element ________ is [Kr]5s24d10
- Fe
- Cd
- Cr
- Mn
- Zn
The ground-state electron configuration of ________ is [Ar]4s23d7.
- Ti
- Co
- Fe
- Cr
- Cs
Chlorine has the following ground-state configuration:
- [He]3s23p2
- [Ne]3s23p5
- [He]2s22p5
- [Ne]2s22p3
- [He]3s23p5
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in each d-subshell?
- 10
- 5
- 6
- 3
- 2
What noble gas core should be used when writing the condensed electron configuration of Strontium (Sr)?
- [Xe]
- [Kr]
- [Ne]
- [Ar]
- [He]
Electron Configuration of Ions
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of S2-?
A) [Ne]
B) [Ne]3s23p6
C) [Ne]3s23p4
D) [Ne]3s23p2
E) [Ne]4s2
A cation of +3 indicates that an element has
A) lost three neutrons.
B) lost three protons.
C) lost three electrons.
D) gained three protons.
E) gained three electrons.
Indicate the ground state electron configuration for Cl⁻.
A) 1s22s22p63s23p4
B) 1s22s22p63s23p5
C) 1s22s22p63s23p6
D) 1s22s22p63s13p6
E) 1s22s22p63s33p5
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Ba2+ ?
A) [Kr]5s24d105p66s2
B) [Kr]5s24d105p6
C) [Kr]5s24d105p65d2
D) [Kr]5s25p6
E) [Kr]5s24d105p66s2
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Ti2⁺.
A) [Ar]3d4
B) [Ar]3d2
C) [Ar]4s2
D) [Ar]4s23d4
E) [Ar]4s23d2
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Zn2⁺?
A) [Ar]4s23d6
B) [Ar]3d10
C) [Ar]4s23d8
D) [Ar]3d8
E) [Ar]
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Cr3⁺?
A) [Ar]
B) [Ar]4s13d2
C) [Ar]3d3
D) [Ar]4s23d1
E) [Ar]4s23d7
How many valence electrons are present in the azide (N3-) ion?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 8
D) 7
E) 2
Ca2+ has the following ground state electron configuration:
A) 1s22s22p6
B) 1s22s22p63s2
C) 1s22s22p63s23p2
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d2
E) 1s22s22p63s23p6
Rb+ has the following ground state electron configuration:
A) [Kr]5s24d6
B) [Kr]4s2
C) [Ar]4s24p4
D) [Kr]5s1
E) [Ar]4s23d104p6
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Fe3⁺?
A) [Ar]3d5
B) [Ar]4s13d3
C) [Ar]
D) [Ar]4s23d9
E) [Ar]4s23d1
The correct ground state electron configuration for Br– is:
A) [Ar]4s23d104p6
B) [Ar]4s23d104p3
C) [Ar]4s23d84p6
D) [Ar]4s23d104p5
E) [Ar]4s24p6
How many electrons are present in the ground state of Mg2+ ion?
A) 2
B) 6
C) 10
D) 8
E) 12