Definition of acids and bases, identifying them along with the conjugate acid and conjugate base, pH of strong and weak acids and bases, the pH and pOH relationship, Ka and Kb, pKa and Ka correlation, the acid-base properties of salts, identifying the acidity of the salt based on the acid and the base it is prepared from, and calculating the pH of salt solutions. This is what is covered in this summary practice problem set on acids and bases.
The links to corresponding topics are given below:
- Definitions of Acids and Bases
- Acid-Base Reactions
- Acid-Base Titrations
- Conjugate Acid and Conjugate Base
- Autoionization of Water and Kw
- The pH and Acidity
- Acid Strength, Ka, and pKa
- Base Strength, Kb and pKb
- Ka, pKa, Kb, and pKb Relationship
- The pH of a Strong Acid and Base
- pH + pOH = 14
- The pH of a Weak Acid
- The pH of a Weak Base
- ThepH of Polyprotic Acids
- The acidity of a Salt Solution
- The pH of a Salt Solution
- The pH of Salts With Acidic Cations and Basic Anions
Practice
Identifying Acids and Bases
Write the chemical equation for the ionization reaction and the corresponding Ka equilibrium expression for each acid.
(a) HCN, (b) H2S, (c) C5H5NH+, (d) HF
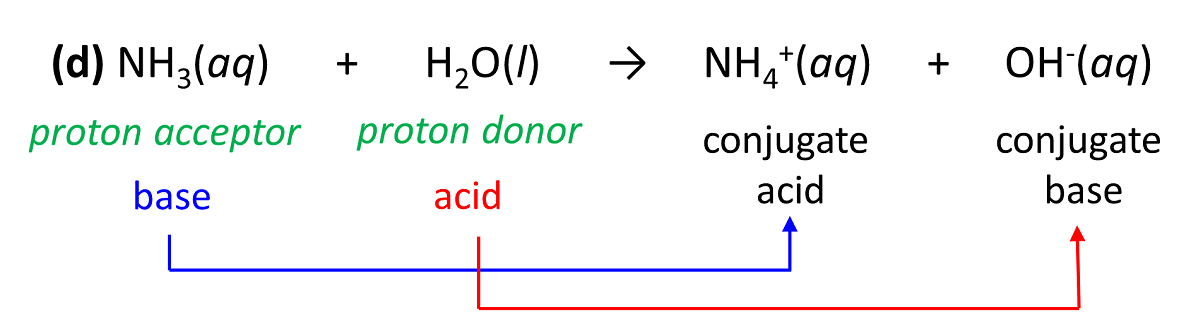
In each reaction, identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and the conjugate base according to the Brønsted–Lowry acid-base theory.
(a) H2SO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + HSO3–(aq)
(b) CH3NH3+(aq) + OH–(aq) → CH3NH2(aq) + H2O(l)
(c) H2PO4–(aq) + NH3(aq) → HPO42-(aq) + NH4+(aq)
(d) NH3(aq) + H2O(l) → NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq)
(e) CH3CH2NH2(aq) + H2O(l) → CH3CH2NH3+(aq) + OH–(aq)
(f) HClO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + ClO3–(aq)
(g) CH3COO2–(aq) + HCN(aq) → CH3COOH(aq) + CN–(aq)
(h) C5H5N(aq) + H2O(l) → C5H5NH+(aq) + OH–(aq)
(i) CO32-(aq) + H2O(l) → HCO3–(aq) + OH–(aq)
(j) HBr(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Br–(aq)
(k) HClO(aq) + CH3NH2(aq) → CH3NH3+(aq) + ClO–(aq)
(l) HCO3–(aq) + C5H5NH+(aq) → H2CO3(aq) + C5H5N(aq)
Acid Strength
Which of the following is the strongest acid: HCl (Ka = 1.3 x 106), CH3CH2NH3+( Ka = 2.5 x 10-11), and H2SO3 (Ka = 5.9 x 10-2)?
Which of the following is the weakest acid: HClO3, HCN, or HC2H3O2?
Given the pKa of each acid, determine the stronger conjugate base:
a) H2SO3 (pKa 1.9) vs CH3COOH (pKa 4.75)
b) HClO3 (pKa < 1) vs H3PO4 (pKa12)
c) HCN (pKa 2.1) vs H2SO4(pKa < 1)
d) HNO2 (pKa 3.2) vs HI (pKa < 1)
Autoionization of Water and pH
Arrange the following solutions in the order of increasing acidity (least acidic to most acidic):
(a) pH = 9.8
(b) pH = 1.2
(c) pH = 4.7
(d) pH = 6.4
Arrange the following solutions in the order of increasing basicity (least basic to most basic):
(a) pOH = 5.2
(b) pOH = 11.6
(c) pOH = 3.4
(d) pOH = 1.9
Calculate the pH for each of the following solutions at 25 oC:
(a) [H3O+] = 1.3 x 10-2 M
(b) [H3O+] = 1.6 x 10-3 M
(c) [OH–] = 1.8 x 10-3 M
Calculate the [OH–] of each of the following solutions at 25 oC. Identify the solution as neutral, acidic, or basic.
a) [H+] = 2.5 x 10-6 M
b) [H+] = 8.3 x 10-4 M
c) [H+] = 4.6 M
d) [H+] = 3.9 x 10-2 M
Given the pH values, calculate [H3O+] and [OH–] for each solution at 25 oC. Identify each solution as neutral, acidic, or basic.
a) pH = 7.20
b) pH = 15.3
c) pH = 4.60
The pH of Strong Acids and Bases
Calculate the pH for each of the following solutions:
(a) 0.15 M HCl
(b) 0.60 M HClO4
(c) 1.4 M KOH
Calculate the pH of each of the following solutions:
(a) 0.0025 M HI, (b) 0.84 M NaOH
Calculate the pH of the solution prepared by dissolving 24.0 g of HCl in 662 mL of water.
How many grams of KOH is needed to prepare a 680.0 mL solution with a pH of 9.80?
Calculate the pH of the solution prepared by diluting 40.0 mL of 3.00 M HNO3 with 210.0 mL of water.
The pH of Weak Acids
Calculate the pH of a 0.45 M solution of HCN. Ka (HCN) = 4.9 x 10-10
Calculate the pH of a 0.74 M solution of acetic acid. Ka (CH3CO2H) = 1.7 x 10-5
0.86 g benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H, Ka = 6.4 x 10-5) was dissolved in enough water to make 1.0 L of solution. Calculate the pH and concentration of all species present in the solution.
Calculate the pH of a 2.0 M solution of hydrofluoric acid, HF if Ka (HF) = 6.6 x 10-4
What is the acid ionization constant (Ka) of a weak acid (HA) if its 0.246 M solution has a pH of 2.68?
A solution of nitrous acid (HNO2, Ka = 7.2 x 10-4) has a pH of 3.1. What was the initial concentration of nitrous acid in the solution?
Calculate the pH of a 0.40 M H2S solution given that Ka1 = 1.0 x 10-7; Ka2 = 1.0 x 10-19.
The pH of Weak Bases
Explain why all of these are weak bases by writing the equations for their reaction with water and the corresponding expression for Kb.
(a) NH3 (b) HCO3– (c) CN- (d) CH3NH2 (e) C5H5N (f) F–
Determine the pH of a 0.85 M solution of ammonia (NH3).
Triethylamine, (C2H5)3N is a common organic weak base with Kb of 4.0 x 10-4 . Calculate [OH–], [H+], and the pH of 0.25 M solution of triethylamine.
Calculate [OH–], [H+], and the pH of 0.40 M solution of caffeine (pKb = 10.4).
Calculate the percentage of ethyl amine (CH3CH2NH2) that is ionized by reacting with water in its 0.64 molar aqueous solution (Kb = 5.6 x 10-4).
Morphine is among the most popular alkaloids that are used as pain killers. Like all the others, it contains a nitrogen atom which makes it a weak base. What is the Kb of morphine at a certain temperature if its 0.340 M solution has a pH of 10.9?
The Acid–Base Properties of Salts
For each ion, determine if it acts as a weak base in an aqueous solution. For those that do, write an equation to show why they make the solution basic.
a) Cl– b) BrO– c) CN– d) ClO3– e) CH3CO2– f) I– g) NO2– h) F–
Predict whether the aqueous solutions of the following compounds are acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) KBr (b) FeCl2, (c) Na2CO3, (d) Al(NO3)3 (e) KClO4, (f) Na2SO3, (g) NH4ClO3
Which of the following salts would produce the most basic aqueous solution?
KF b. NaBr c. NH4Cl d. MgCl2 e. Mg(NO3)2
Calculate the pH of a 0.74 M solution of NaOBr (Ka HBrO = 2.90 x 10-9).
Calculate the pH of the 0.26 M solution of NH4ClO3 (Kb NH3 = 1.8 x 10-5).
Calculate the pH of a 0.35 M solution of KNO2 (Ka = 4.0 x 10-4).
Calculate the pH of a 1.0 M solution of sodium acetate (CH3CO2Na) considering that the Ka of acetic acid (CH3CO2H is 1.7 x 10-5.