In the previous post, we discussed converting grams to moles. Remember, the first thing was to look up the molar mass in the periodic table, set up the correct conversion factor, and finally do the multiplication. Here is a short summary for converting the mass to moles:
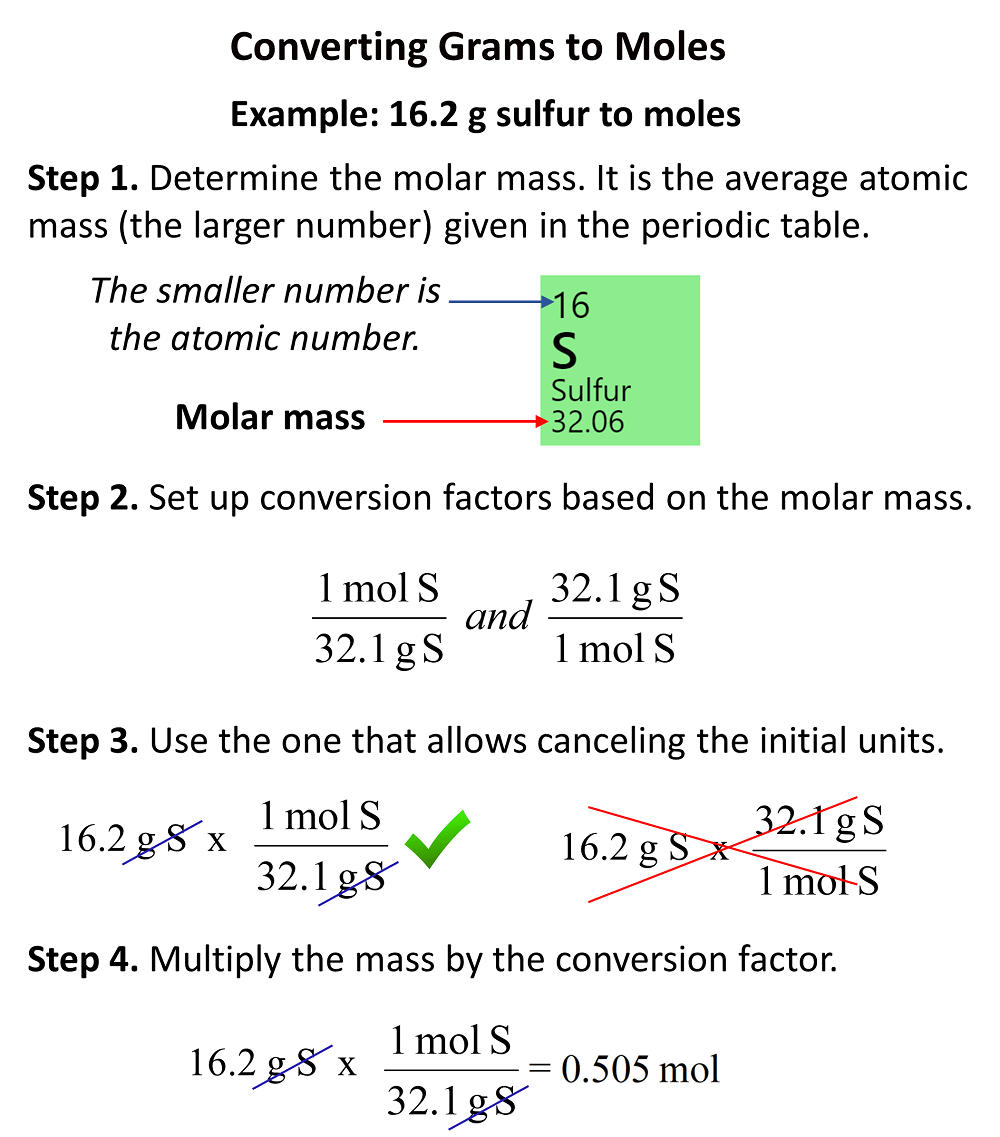
Now, to calculate the number of molecules or atoms from mass, we need one extra step using the Avogadro’s number (6.02 x 1023). Remember, the Avogadro’s number shows how many particles, which can be atoms, molecules, ions, there are in one mole of a sample and because it is related to moles, we need to first convert the mass to moles.
So, there are two steps combined in this conversion and the plan is to first convert the mass to moles and then to the number of molecules using NA:
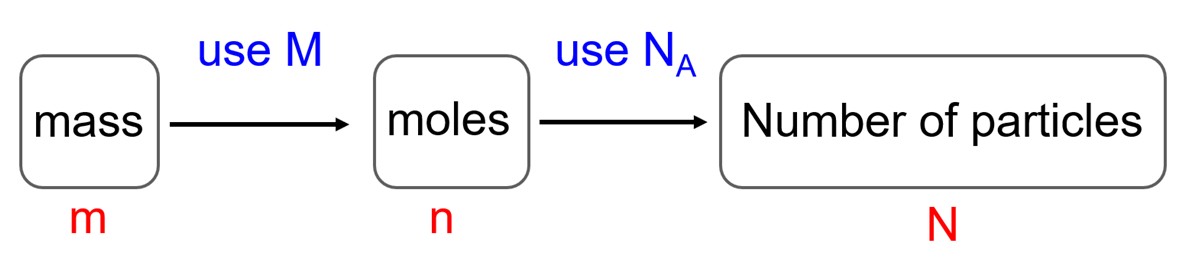
For example, how many molecules of PCl5 are there in a 54.0 g of sample?
First, we calculate the molar:
M (PCl5) = M (P) + 5 M (Cl) = 31.0 + 5 x 35.5 = 208.5 g/mol
The two conversion factors for calculating the moles would be:
\[\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\;{\rm{or}}\,\,\frac{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\]
We are going to use the first conversion factor because it has the units of grams on the denominator which allows us to cancel them with the initial amount given in grams:
\[{\rm{n}}\,{\rm{(PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{)}}\,{\rm{ = }}\,{\rm{54}}{\rm{.0}}\,\cancel{{{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}}\;{\rm{ = }}\,{\rm{0}}{\rm{.260}}\,{\rm{mol}}\]
Once we have the number of moles, we use another conversion factor linking it with the Avogadro’s number.
\[\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{\rm{molecules}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\;{\rm{or}}\,\frac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{\rm{molecules}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\]
And this time, we need to pick the one that allows canceling the mols which is the second conversion factor:
\[{\rm{0}}{\rm{.26 }}\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\, \times \;\frac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{\rm{molecules}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}}\, = \;1.57\,{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\,{\rm{molecules PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}\]
You can always combine the conversions into a one-step process:
\[{\rm{N}}\,{\rm{(PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{)}}\,{\rm{ = }}\,{\rm{54}}{\rm{.0}}\,\cancel{{{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}}\; \times \;\frac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{\rm{molecules}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}}\, = \;1.57\,{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\,{\rm{molecules}}\]
Another example: How many molecules of glucose, C6H12O6 are there in a 35.0 g sample?
The molar mass of glucose is:
M (C6H12O6) = 6 x 12 + 12 x 1.0 + 6 x 16 = 180 g/mol
Therefore, the two conversion factors for going mass → moles, and moles → molecules are:
\[\frac{{{\rm{1}}\,{\rm{mol}}\,{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}}}{{{\rm{180}}{\rm{.}}\,{\rm{g}}}}\;,\,\,\frac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.022}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}\,{\rm{molecules}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\,{\rm{mol}}\,{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}}}\]
So, we can use these factors to convert the mass to the number of molecules:
\[{\rm{N}}\;{\rm{(}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{)}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{35}}{\rm{.0}}\cancel{{\rm{g}}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{1}}\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\,{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}}}}}{{{\rm{180}}{\rm{.}}\cancel{{\rm{g}}}}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.022}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}\,{\rm{molecules}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\,\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\,{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}}}}}\; = \;1.17\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;\;\;\]
Converting the Number of Molecules to Grams
Sometimes, you may be asked to determine the mass of a sample given the number of molecules. This is the reverse calculation, and we are going to use the other conversion factor that we obtain for linking the molar mass to moles, and the moles to the number of molecules.
For example, let’s say we were asked to determine the mass of a PCl5 sample that contains 7.58 x 1024 molecules. Remember, these were the conversion factors we got for finding the number of molecules for a PCl5 sample:
\[\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\;{\rm{or}}\,\,\frac{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\]
\[\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{\rm{molecules}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\;{\rm{or}}\,\frac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;{\rm{molecules}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\]
This time, we are starting with the conversion factor containing the Avogadro’s number, and we need to pick the one that allows canceling the number of molecules, and then then the number of moles.
\[{\rm{m}}\,{\rm{(PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{)}}\,{\rm{ = }}\,{\rm{7}}{\rm{.58}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{24}}}}\cancel{{{\rm{molecules}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{1}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}}{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.02}}\;{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{23}}}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{molecules}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,\frac{{{\rm{208}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{g}}\,{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}{{{\rm{1}}\;\cancel{{{\rm{mol}}\;{\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\,}}\,{\rm{ = }}\;{\rm{2}}{\rm{.63}}\,{\rm{ \times }}\,{\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{\rm{3}}}\,{\rm{g}}\]
Practice
Calculating Moles from Mass
Determine the number of moles in 59.7 grams of Al.
Determine the number of moles in 2.41 grams of FeO.
Calculate the number of moles in 0.647 grams of Al2O3.
Determine the number of moles in 3.56 grams of Mg(OH)2.
Determine the number of moles in 0.385 grams of N2O3.
Determine the number of moles in 165 grams of CaSO4.
Calculate the molar mass of N2O4 and determine how many moles of it are in a 23.9 g sample.
Calculate the number of moles in 165 grams of C3H6O.
Determine the number of moles in 452 grams of Co(NO3)3.
Calculating Mass from Moles
Calculate the mass in grams of 0.598 moles of Fe.
Calculate the mass in grams of 0.168 moles of NO.
Calculate the mass in grams of 0.987 moles of (NH4)2S.
Calculate the mass in grams of 6.81 moles of Al2(SO4)3.
Calculate the mass in grams of 2.64 moles of methanol, CH3OH.
Calculate the mass in grams of 9.42 moles of NiCl2·6H2O.
Calculating the Number of Molecules from the Moles
How many molecules are there in a 0.487 mol sample of PCl5?
How many molecules (formula units) are there in a 5.84 mol sample of Na2SO3.
How many molecules of sucrose, C12H22O11 are there in a 0.684 mol sample?
Calculate the number of molecules in a 3.25-mol sample of propane, C3H8.
How many moles is 5.80 x 1025 molecules of POCl3?
Calculating the Number of Molecules from the Mass
How many molecules are there in a 5.12-g sample of K2O?
Calculate the number of molecules of butane, C4H10, in its 2.40-gram sample.
How many Ethylene, C2H4 molecules are present in a 46.2 g sample? The molar mass of C2H4 is 28.0 g/mol.
Calculating the Number of Atoms
Calculate the number of atoms in a 2.56-mol sample of Ca.
How many carbon atoms are there in a 0.590 mol sample of CCl4.
How many carbon atoms are there in a 0.964 mol sample of C2H6.
Which sample contains a more Cl atoms: a) 1.25 moles of CH2Cl2 b) 2.15 moles of CH3Cl
The molecular formula of morphine is C17H19NO3. How many carbon atoms are in a 34.7-gram sample of morphine?
Isopropyl alcohol, also known as isopropanol, has found a widespread application in the preparation of pharmaceutical products. Answer the following questions considering that the molecular formula of isopropanol is C3H8O.
a) How many moles of C3H8O are contained in a 12.0 g sample of the alcohol?
b) How many molecules of C3H8O are contained in a 12.0 g sample of the alcohol?
c) How many atoms of oxygen are contained in a 12.0 g sample of the isopropyl alcohol (C3H8O)?
d) How many atoms of carbon are contained in a 12.0 g sample of the isopropyl alcohol (C3H8O)?
Check Also
- Subatomic particles and Isotopes
- Naming Monatomic and Polyatomic Ions
- Naming Ionic Compounds
- Naming Covalent Compounds
- Naming Acids and Bases
- Atomic and Molecular Masses
- The Mole and Molar Mass
- Percent Composition and Empirical Formula
- Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
- Limiting Reactant
- Limiting Reactant Practice Problems
- Reaction/Percent Yield
- Stoichiometry Practice Problems