All the equations where the reactants and products are shown as molecules with complete chemical formulas are called molecular equations. This, essentially, is what we use for most reactions. For example:
2K3PO4(aq) + 3BaCl2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6KCl(aq)
However, we know that water-soluble ionic compounds dissociate into ions. Equations with all the soluble reactants and products dissociated into ions are called ionic equations.
When we show the electrolyte dissociated into ions, the ionic equation is obtained.
So, for the reaction above, we need to use the table for the solubility of inorganic compounds and determine which components need to be dissociated:
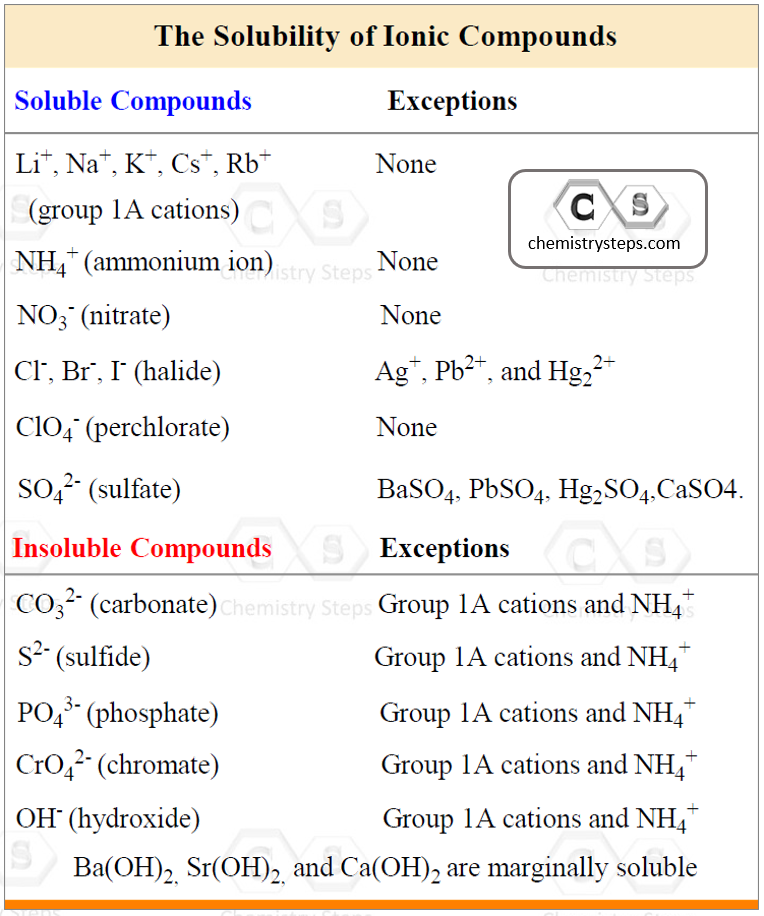
- K3PO4 and KCl are soluble because all the salts of group 1A cations are water-soluble.
- BaCl2 is soluble because halides are soluble with the exception of their Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg22+
- Ba3(PO4)2 is insoluble because the phosphate ion falls in the category of making insoluble salts unless combined with alkali metals and ammonium ion.
Therefore, the ionic equation for this reaction is:
6K+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) + 3Ba2+(aq) + 6Cl–(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6K+(aq) + 6Cl–(aq)
Important! Solids (precipitates), liquids, and gases do not dissociate, and we always write them in molecular forms.
Notice that some ions appear on both sides of the ionic equation. These are called spectator ions because they do not play a direct role in the reaction:
6K+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) + 3Ba2+(aq) + 6Cl–(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6K+(aq) + 6Cl–(aq)
Spectator ions
To show the overall chemical transformation, we omit the spectator ions, and the resulting equation is called the net ionic equation:
3Ba2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s)
Check Also
- Solutions
- Strong and Weak Electrolytes
- Dissociation of Ionic Compounds
- Molarity
- Dilution
- Ion Concentration
- Precipitation Reactions
- Definitions of Acids and Bases
- Acid-Base Reactions
- Stoichiometry of Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
- Acid-Base Titrations
- Oxidation State
- Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
- Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Practice Problems
Practice
Write balanced complete ionic and net ionic equations for each reaction:
a) K2SO4(aq) + CaCl2(aq) →CaSO4(s) + 2KCl(aq)
b) Na2S(aq) + 2HBr(aq) → 2NaBr(aq) + H2S(g)
c) NH4Cl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + NH3(g)
d) Na2CO3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + CO2(g)+ H2O(l)
e) AgNO3(aq) + NaI(aq) → Agl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
f) HBr(aq) + KOH(aq) → KBr(aq) + H2O(l)
g) HC2H3O2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → NaC2H3O2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
h) LiOH(aq) + HC2H3O2(aq) → LiC2H3O2(aq) + H2O(l)
i) HCl(aq) + NH3(aq) → NH4Cl(aq)
j) 2K3PO4(aq) + 3BaCl2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6KCl(aq)