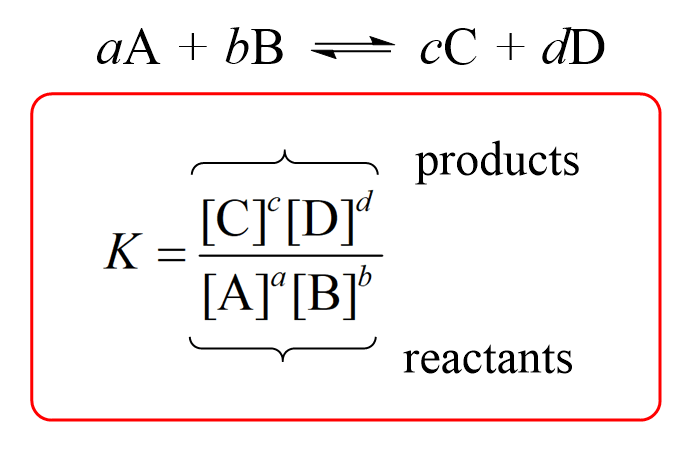
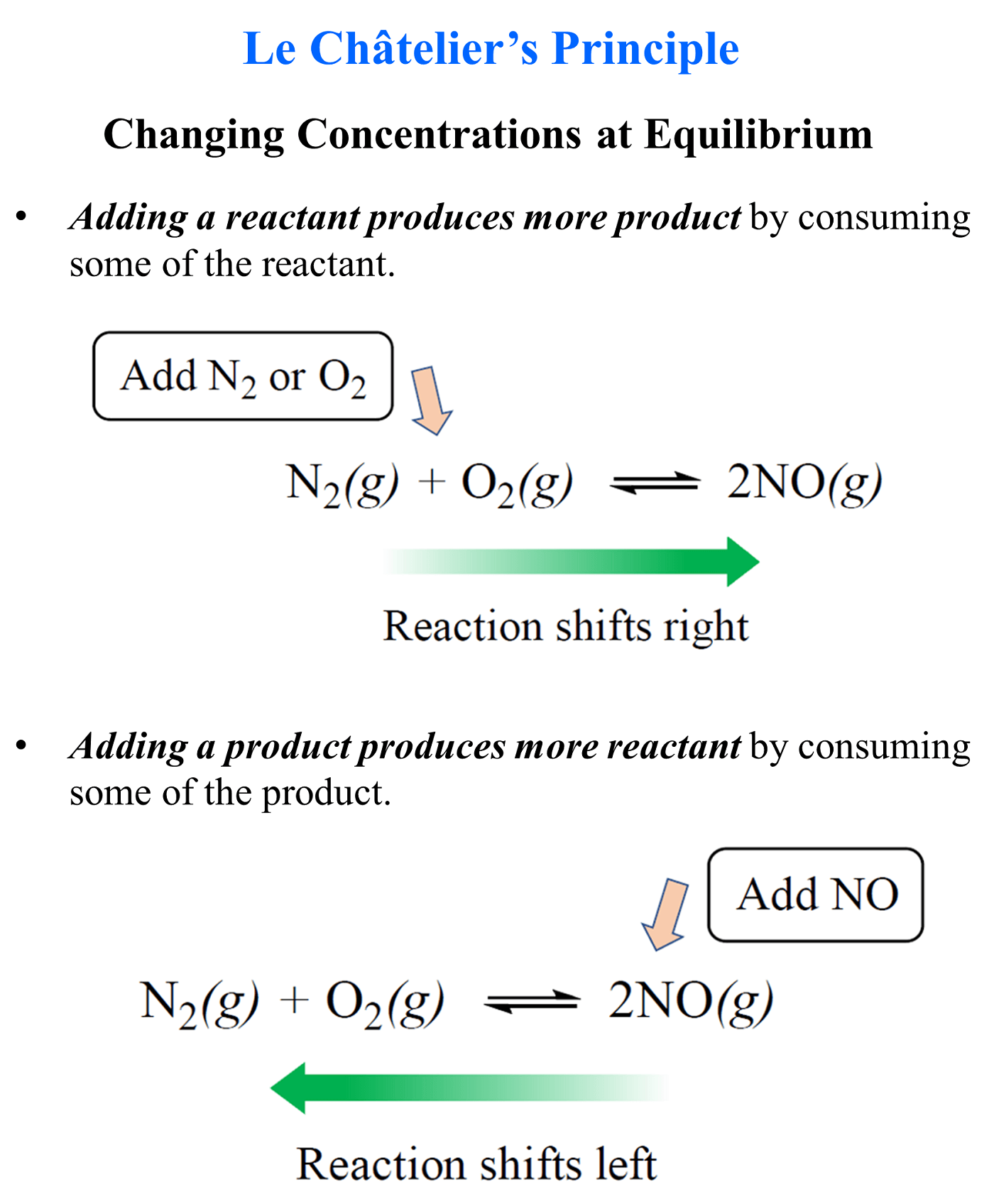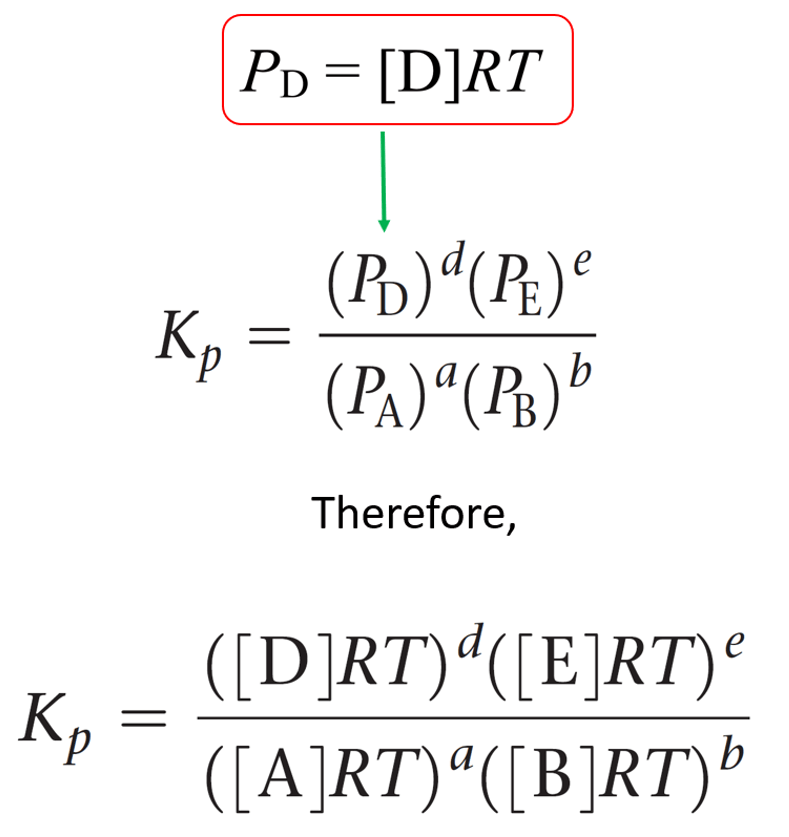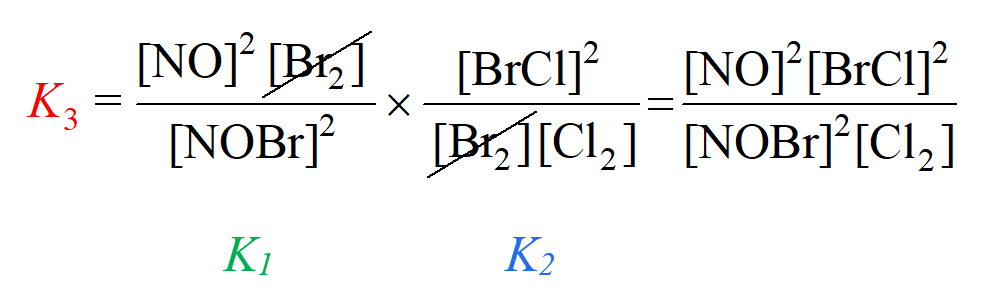Le Chateliers Principle Practice Problems
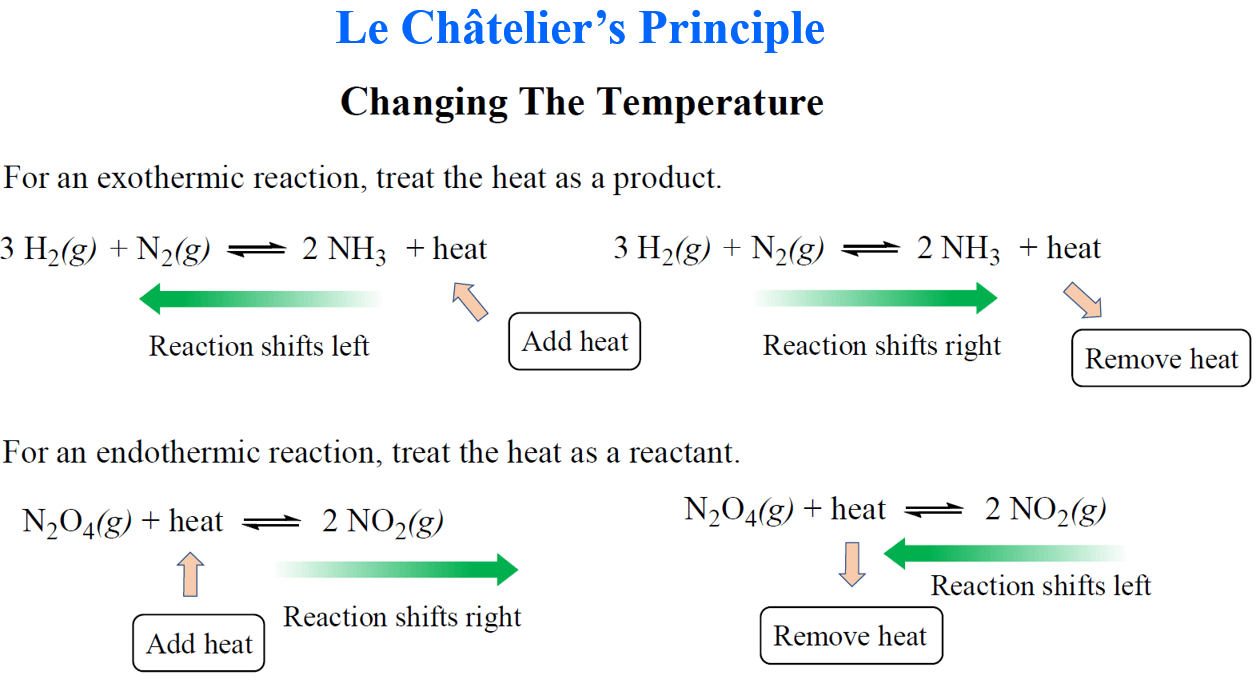
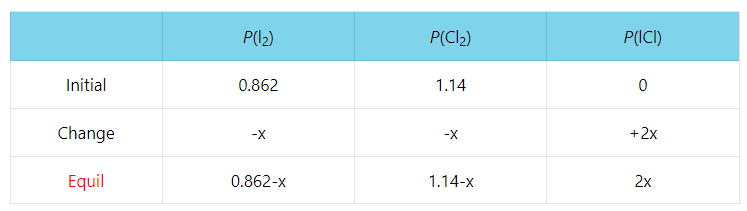
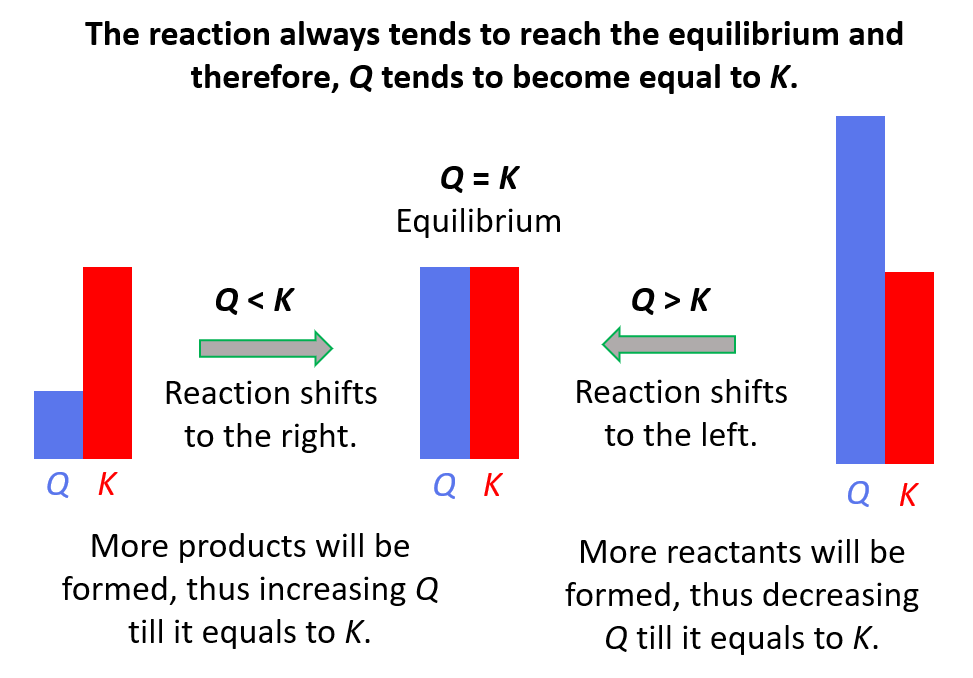
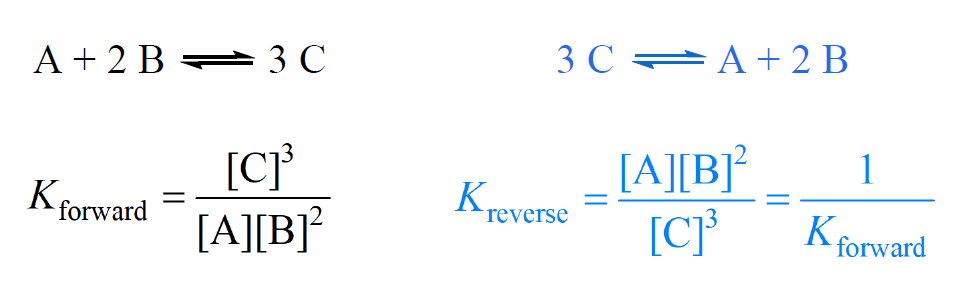
In the previous post, we talked about Le Châtelier’s principle that helps evaluate the effect of changing the concentrations, volume, pressure, and temperature on the equilibrium. In short, you need to remember that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, … Read more