This equilibrium practice problem set includes questions on writing the equilibrium constant of given chemical reactions, determining the value of the equilibrium constant based on the concentrations and partial pressures of gases, deriving a new expression for an equilibrium constant from separate reactions, converting between Kc and Kp, calculating the quotient and determining the course of the reaction, calculations of concentrations based on the quotient and equilibrium constant, as well as working on equilibrium reactions based on the Le Châtelier’s principle.
The links to the corresponding articles are provided herein:
- Chemical Equilibrium
- Equilibrium Constant
- Kpand Partial Pressure
- Kp and KcRelationship
- K Changes with Chemical Equation
- Equilibrium Constant K from Two Reactions
- Reaction Quotient – Q
- ICE Table – Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
- ICE Table Practice Problems
- Le Châtelier’s principle
- Le Châtelier’s principle Practice Problems
- Chemical Equilibrium Practice Problems
Practice
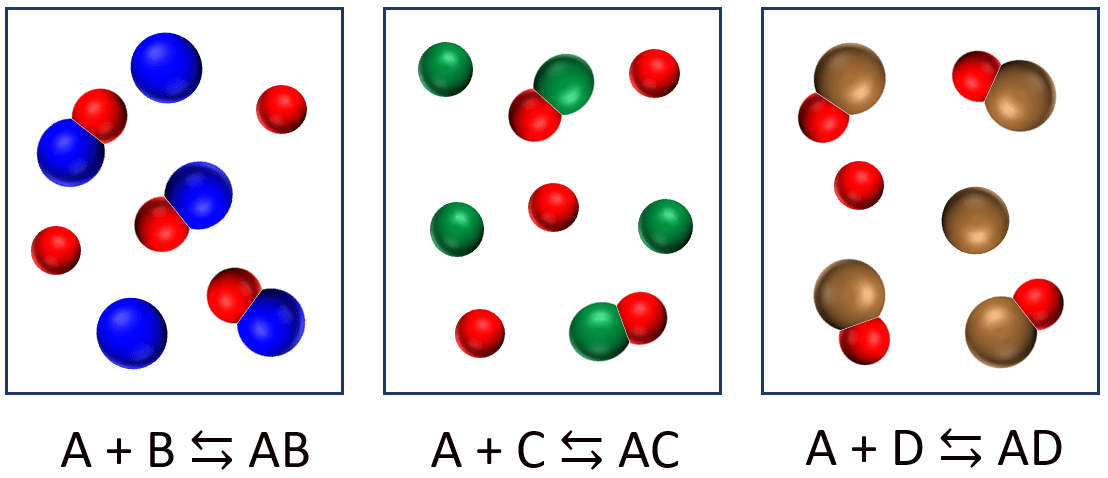
Consider this reaction at equilibrium:
N2 + O2(g) ⇆ 2NO(g)
Predict whether the reaction will shift left, shift right, or remain unchanged after each disturbance.
a) NO is added to the reaction mixture.
b) N2 is added to the reaction mixture.
c) NO is removed from the reaction mixture.

it is very helpful
Glad to hear that. Thanks.